bottom
|
Shanghai Academy of Spaceflight Technology Powered by www.300.cn 沪ICP备15011809号 |
New Detail
FENGYUN Satellite User Conference | Witness the Successful Debut of FY-3G
2023 FENGYUN Satellite User Conference (FYSUC) was held on May 15 in Changzhou, Jiangsu Province. Themed by “Construct a precision meteorological monitoring system and promote the application of Fengyun Satellite”, FYSUC of this year aimed to thoroughly implement the important instructions on meteorological work of Xi Jinping, general secretary of the Communist Party of China and the spirit of the Guideline on Fostering the High-quality Development of Meteorology (2022-2035), promote exchange and cooperation between users of different industries and areas, and enhance the supportability of FENGYUN satellite to life safety, production development, life affluence, and ecological soundness.
In the conference, the first set of images of FENGYUN-3G (FY-3G) (precipitation satellite), China’s first inclined-low-orbit precipitation measurement satellite generally developed by Shanghai Aerospace Technology Institute, were officially released to the public. The monitoring images of 6 payloads onboard FY-3G showed the three-dimensional structure of different layers of precipitation, which can enable better monitoring and forecasting of severe precipitation systems.
The 6 payloads onboard FY-3G include 4 business payloads of Precipitation Measurement Radar, Microwave Radiation Imager-Rainfall Mission, Medium Resolution Spectral Imager - Rainfall Mission, and GNSS Radio Occultation Sounder, and 2 testing payloads of short-wave infrared Polarized Multi-Angle Imager and High Accuracy On-board Calibrator.
There was a severe convective weather system in South China on May 7, for which the Central Meteorological Observatory issued blue alert for heavy rain and blue alert for severe convective weather. FY-3G clearly captured the three-dimensional structure of this rain-bearing cloud system.
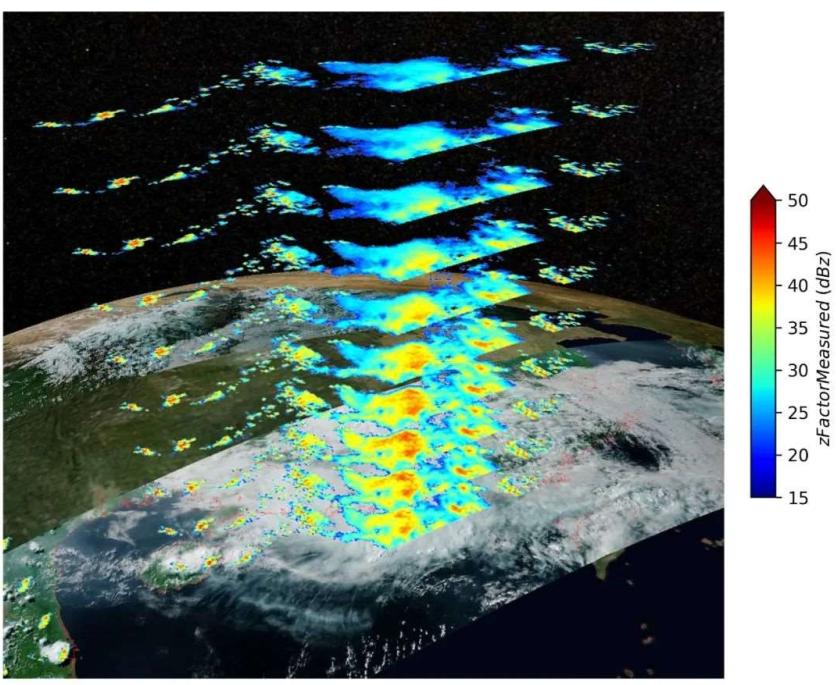
At 16:35 on May 7, the precipitation measurement radar onboard FY-3G captured the rain near Hainan and Yangjiang in Guangdong. The image showed the three-dimensional structure of the precipitation system from 3.75 kilometers to 6 kilometers from the surface. Credits: National Satellite Meteorological Center of CMA
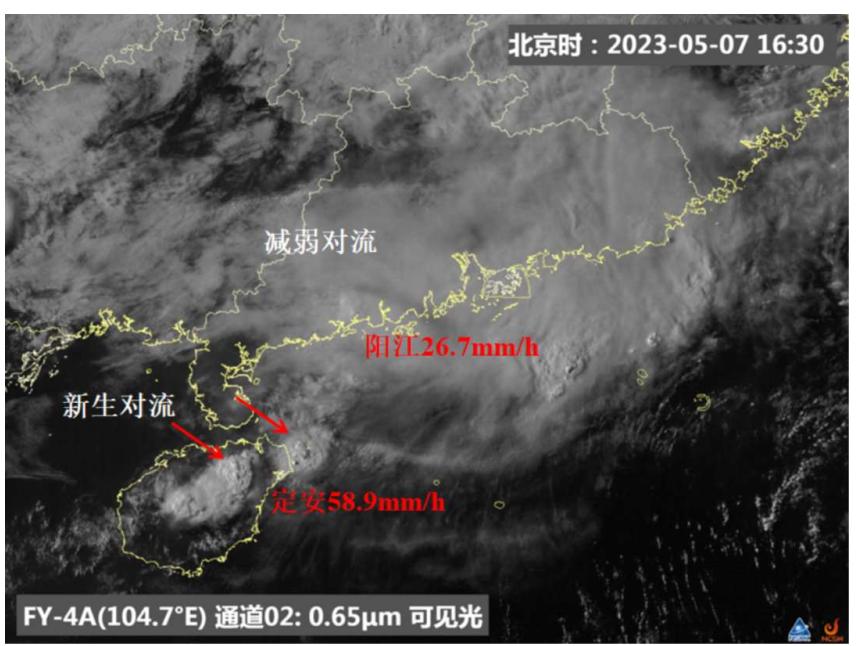
Affected by the low level shear line of the end of frontal cyclone cloud system moving east toward the ocean, there was a severe convective cloud system in the day on May 7 in South China. In the afternoon, the severe convection in Guangdong gradually moved east and weakened, and new convection was triggered in north Hainan to the southwest of Guangdong. At 16:00 to 17:00, the maximum hourly precipitation in south Guangdong was 26.7mm, and 58.9mm in north Hainan. Credits: National Satellite Meteorological Center of CMA
The precipitation measurement radar is the main payload onboard FY-3G, also the first precipitation measurement radar onboard in China, which is mainly used for precipitation monitoring of severe weather systems. It has adopted Ku + Ka-band dual-frequency and can clearly observe the internal three-dimensional structure of precipitation systems like typhoon, rainstorm and blizzard.

FY-3G displayed the three-dimensional structure of the precipitation area in multiple angles. Credits: National Satellite Meteorological Center of CMA
Microwave radiation imager-rainfall mission onboard FY-3G is the upgrade of that onboard FY-3C and FY-3D, realizing the integrated design of atmospheric window and detection channel for the first time. With up to 26 channels, it effectively enhances the detection capacity of the satellite in terms of precipitation and atmospheric temperature and humidity profiles. It mainly utilizes the micro-wave channels set at the atmospheric window and near the oxygen and moisture absorption line to capture the data of hydrometeor in the precipitation cloud for synergistic retrieval of the precipitation data.

Collage of orbiting animation by Micro-Wave Radiation Imager - Rainfall Mission. Credits: National Satellite Meteorological Center of CMA
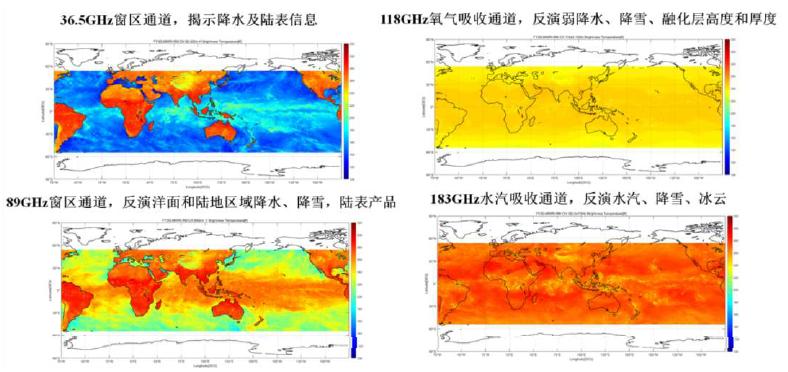
Collage of the brightness temperatures in middle and low latitudes areas around the globe detected by the Micro-Wave Radiation Imager - Rainfall Mission from May 2 to 5. Credits: National Satellite Meteorological Center of CMA
The Medium Resolution Spectral Imager - Rainfall Mission firstly realized the earth observation with 500-m spatial resolution from sub satellite points of all channels of meteorological satellite optical imager in China, and the visible light cloud pictures clearly showed the fine cloud top structure of the convective cloud clusters.
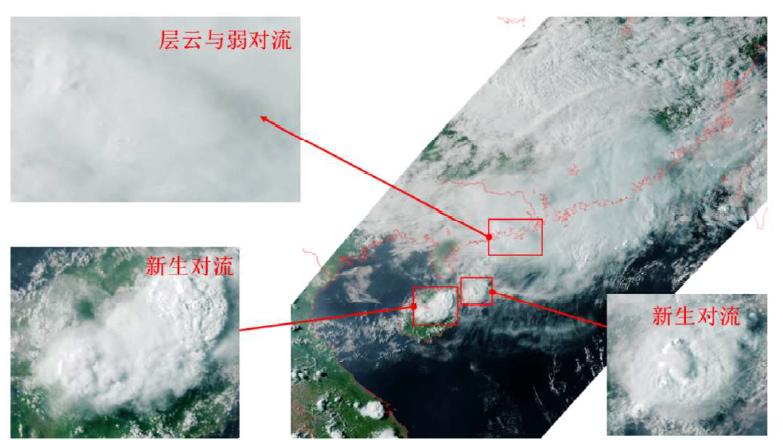
Pseudo color collage for southeast coastal area of China at 8:35 on May 7 captured by the Medium Resolution Spectral Imager - Rainfall Mission. Credits: National Satellite Meteorological Center of CMA
GNSS Radio Occultation Sounder (GNOS-II) can receive occultation signals from Beidou and GPS, with over 500 pieces of atmospheric occultation events equally distributed around the globe observed by each of the two navigational systems per day, to provide high accuracy and high vertical resolution atmospheric bending angle, atmospheric refraction index, atmospheric temperature, and atmospheric humidity profile in the troposphere and stratosphere for numerical weather prediction and climate monitoring. Its sea surface normalized radar scattering cross-section and land surface reflectance can provide data of sea surface wind speed in severe weather such as typhoon and data of soil humidity with high spatial resolution.

The occultation distribution graphs from Beidou (BDS) and GPS received by GNOS-II. Credits: National Satellite Meteorological Center of CMA

The sea surface normalized radar scattering cross-section and land surface reflection monitored by GNOS-II. Credits: National Satellite Meteorological Center of CMA
The test payload of short-wave infrared Polarized Multi-Angle Imager onboard FY-3G firstly realized the polarized multi-angle satellite observation capacity of the short-wave infrared band in China. The polarization data obtained by it shows unique “cloud bow” characteristic, which can be applied in identifying water clouds and retrieving the effective radium of cloud droplet to enhance the monitoring capacity in the fields of weather forecast, climate change and earth environment.
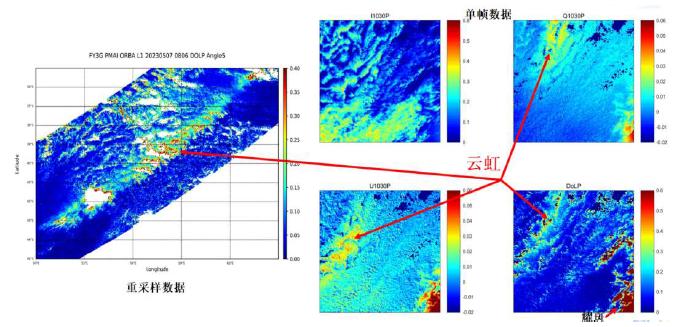
Polarization data obtained by the short-wave infrared Polarized Multi-Angle Imager showed unique “cloud bow” characteristic. Credits: National Satellite Meteorological Center of CMA
High Accuracy On-board Calibrator conducted in-orbit solar cross-calibration technical verification testing for the first time. It utilizes the solar cross-calibration technology to acquire high-accuracy Earth reflectance data, and is equipped with the capacity to provide spatial radiation calibration criterion for other visible/near-infrared instruments.
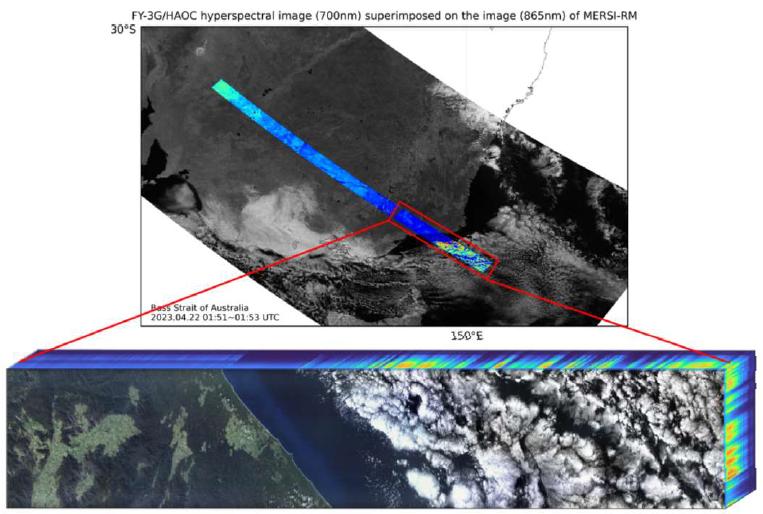
On April 22, the High Accuracy On-board Calibrator flew over the Bass Strait in Australia and obtained the first set of visible/near-infrared hyperspectral image cubes. Credits: National Satellite Meteorological Center of CMA
It is reported that FY-3G was successfully launched from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center at 9:36 a.m. on April 16. It is the third active precipitation measurement satellite in the world after the United States and Japan’s joint launch of satellites specific for precipitation measurement. The successful launch of FY-3G marks that China has become the only country in the world which operates meteorological satellites in four near-earth orbits, i.e. early morning, midmorning, afternoon and inclined orbits.

